A fasting blood sugar level of 119 mg/dL is considered prediabetic. This indicates a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health. A fasting blood sugar test measures glucose after an overnight fast. Levels between 100-125 mg/dL are classified as prediabetes, signaling a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It is essential to monitor and manage blood sugar to prevent complications.
Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help maintain optimal levels. Consulting a healthcare provider for personalized advice is also important. Early detection and management can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes and improve quality of life.
Credit: researchoutreach.org
The Significance Of Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting blood sugar levels are critical for overall health. They indicate how well your body manages glucose. High levels may signal health issues. Understanding these levels helps maintain good health.
Normal Ranges For Fasting Glucose
Normal fasting glucose levels vary. For most people, the normal range is:
- 70 to 99 mg/dL: Normal fasting glucose
- 100 to 125 mg/dL: Prediabetes range
- 126 mg/dL and above: Diabetes range
A fasting blood sugar of 119 mg/dL falls in the prediabetes range. It requires attention and lifestyle changes.
Implications Of Elevated Fasting Glucose
Elevated fasting glucose can affect your health. Here are some implications:
- Increased Risk of Diabetes: High fasting glucose often leads to diabetes.
- Heart Disease: Elevated levels can increase heart disease risk.
- Nerve Damage: Persistently high glucose can damage nerves.
- Kidney Issues: High levels may harm kidneys over time.
- Vision Problems: Long-term high glucose can affect your vision.
Monitoring fasting blood sugar is essential for preventing complications. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help manage levels effectively.
| Fasting Blood Sugar Level | Implication |
|---|---|
| 70-99 mg/dL | Normal |
| 100-125 mg/dL | Prediabetes |
| 126 mg/dL and above | Diabetes |
Interpreting A 119 Mg/dl Blood Sugar Reading
Understanding a 119 mg/dL blood sugar reading can be crucial for your health. This article explains what this number means, what influences it, and how you can manage it.
Blood Sugar Metrics Explained
Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). A fasting blood sugar reading is taken after an overnight fast. The American Diabetes Association provides the following guidelines:
| Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Below 70 | Hypoglycemia (Low) |
| 70-99 | Normal |
| 100-125 | Prediabetes |
| 126 and above | Diabetes |
A 119 mg/dL reading falls into the prediabetes category. This means your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be diabetes.
Factors That Influence Readings
Many factors can influence your fasting blood sugar levels:
- Diet: Consuming sugary foods can spike blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Physical activity can lower blood sugar.
- Medications: Some drugs can affect blood sugar readings.
- Stress: High stress levels can increase blood sugar.
- Sleep: Poor sleep can negatively impact blood sugar levels.
Monitoring these factors can help you maintain a healthy blood sugar level. Knowing what influences your readings helps you take control of your health.
Prediabetes And Diabetes: Understanding The Thresholds
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for health. A fasting blood sugar of 119 mg/dL can signal a potential issue. Understanding prediabetes and diabetes thresholds helps manage and prevent complications.
Defining Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. It acts as an early warning signal.
| Blood Sugar Level | Status |
|---|---|
| 70-99 mg/dL | Normal |
| 100-125 mg/dL | Prediabetes |
A fasting blood sugar level between 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes. This range suggests an increased risk of developing diabetes.
When Does It Become Diabetes?
Diabetes is diagnosed when blood sugar levels are consistently high. The threshold for a diabetes diagnosis differs from prediabetes.
| Blood Sugar Level | Status |
|---|---|
| 126 mg/dL or higher | Diabetes |
A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes. At this stage, managing blood sugar becomes critical to avoid complications.
Regular monitoring and early detection are key to preventing diabetes. Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference.
Credit: labs.selfdecode.com
Causes Behind High Fasting Blood Sugar
Understanding the causes behind high fasting blood sugar is vital. It helps in managing and preventing potential health issues. A fasting blood sugar level of 119 mg/dL is slightly elevated. Identifying the underlying causes can aid in better management and lifestyle adjustments.
Dietary Influences
Diet plays a crucial role in blood sugar levels. Consuming foods high in sugar or refined carbs can spike blood sugar. These foods include:
- Candies
- Sugary drinks
- White bread
- Pastries
Eating large portions or frequent snacking can also elevate levels. A balanced diet with whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins is better. Monitoring carbohydrate intake helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle And Health Conditions
Certain lifestyle choices and health conditions can impact fasting blood sugar. Lack of physical activity leads to weight gain and higher blood sugar. Regular exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently. Stress is another factor that can increase blood sugar levels. Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can be beneficial.
Various health conditions also contribute to high fasting blood sugar. These include:
- Diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Hormonal imbalances
- Chronic illnesses
Medications for other conditions can affect blood sugar levels. Monitoring and consulting with healthcare providers is essential for managing these factors effectively.
` Headings. – Important Keywords Are Bolded. – Content Is Divided Into Short, Easy-to-read Sentences. – Unnecessary Words And Phrases Are Avoided. – The Content Is Seo-optimized, Unique, And Valuable For Readers. – Information Is Presented In An Organized Manner With Paragraphs And Bullet Points.
Managing Elevated Fasting Glucose
Fasting blood sugar of 119 mg/dL is slightly elevated. Managing this can prevent diabetes. Learn about effective strategies below.
Dietary Adjustments
Changing your diet can greatly affect blood sugar levels. Focus on eating whole, unprocessed foods.
- Increase fiber intake by eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Reduce sugary foods and drinks. These spike blood sugar levels.
- Choose lean proteins like chicken, fish, and tofu.
- Avoid refined carbohydrates. Examples are white bread and sugary cereals.
Track your food intake. This helps identify foods that raise your blood sugar.
Exercise And Its Benefits
Regular exercise is crucial for managing blood sugar. Aim for at least 30 minutes daily.
- Walking is a simple and effective exercise.
- Strength training helps build muscle and control glucose levels.
- Yoga can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce stress.
Exercise helps your body use insulin better. It also lowers blood sugar levels.
| Type of Exercise | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Walking | Improves circulation and burns calories. |
| Strength Training | Increases muscle mass and boosts metabolism. |
| Yoga | Reduces stress and improves flexibility. |
Set achievable goals. This keeps you motivated and on track.
Medical Interventions And Monitoring
Managing fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing diabetes. A reading of 119 mg/dL is slightly above normal. It indicates that you need to take control. Medical interventions and regular monitoring can help you manage your blood sugar effectively.
When To Seek Medical Advice
If your fasting blood sugar consistently measures 119 mg/dL or higher, it is time to consult a doctor. Persistent high levels may lead to prediabetes or diabetes. Seek advice if you experience symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, or unexplained weight loss.
Treatment Options For High Fasting Glucose
Doctors may recommend lifestyle changes as the first step. These include:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in vegetables and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
If lifestyle changes are not enough, medication might be necessary. Common medications include:
| Medication | Function |
|---|---|
| Metformin | Reduces glucose production in the liver |
| Sulfonylureas | Increase insulin production |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | Help kidneys remove glucose from the bloodstream |
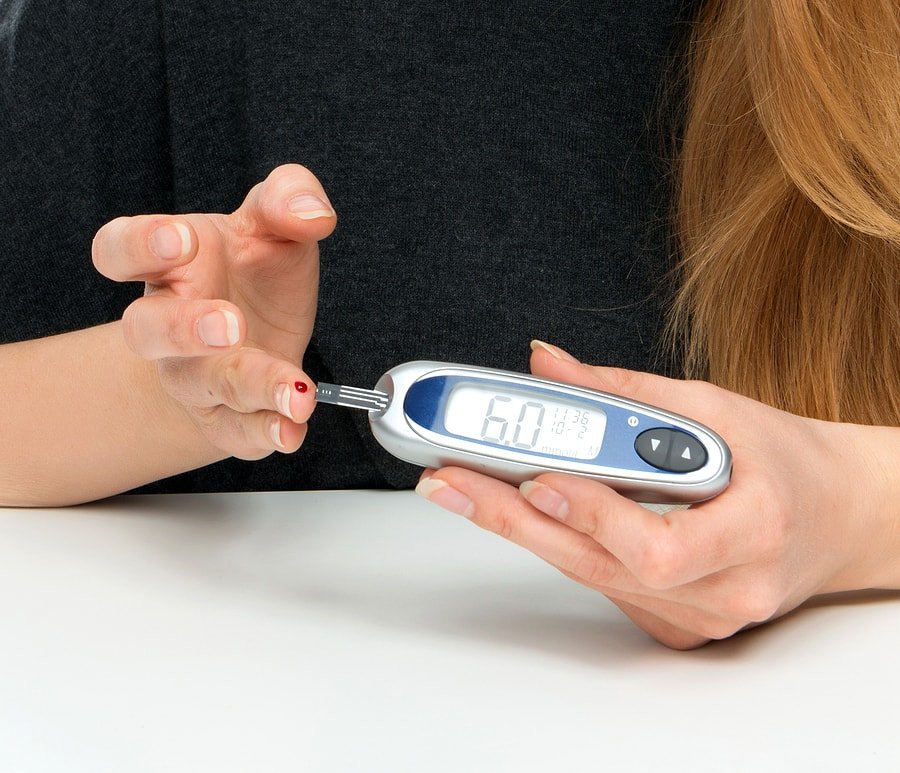
Regular monitoring is essential. Use a home glucose meter to check your levels daily. Record these readings and share them with your doctor. This helps in adjusting treatment plans as needed.
The Role Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems are transforming diabetes care. These devices track blood sugar levels in real-time. CGMs provide detailed data that helps manage diabetes better.
Benefits Of Technology In Glucose Monitoring
Technology offers many benefits for glucose monitoring. CGM systems automatically measure blood sugar levels. This reduces the need for finger-prick tests.
- Real-time data: CGMs provide instant blood sugar readings.
- Trends and patterns: They show blood sugar trends over time.
- Alerts and notifications: CGMs can alert users to highs and lows.
- Convenience: These devices are easy to use and non-invasive.
Interpreting Data For Better Control
Interpreting CGM data is key to better diabetes control. The data can show how food, exercise, and medication affect blood sugar.
- Food choices: Track how different foods impact your levels.
- Exercise: Understand how physical activity affects blood sugar.
- Medication: See how medications influence your glucose.
Doctors can also use CGM data to adjust treatment plans. This leads to more personalized care. Understanding your blood sugar patterns helps you make better decisions. This can improve your overall health.
Credit: templatelab.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What To Do If Fasting Blood Sugar Is 120?
Consult your doctor for personalized advice. Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and monitor your blood sugar levels.
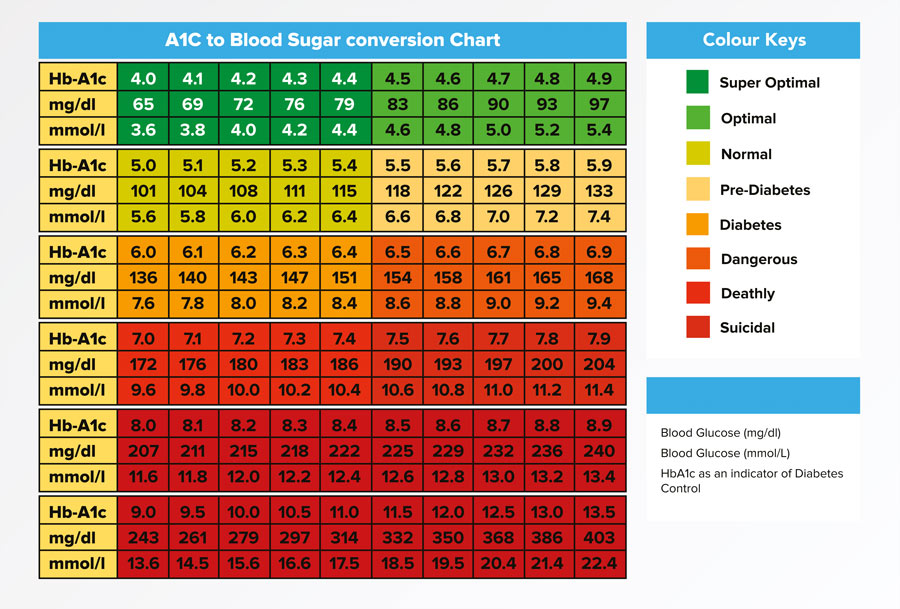
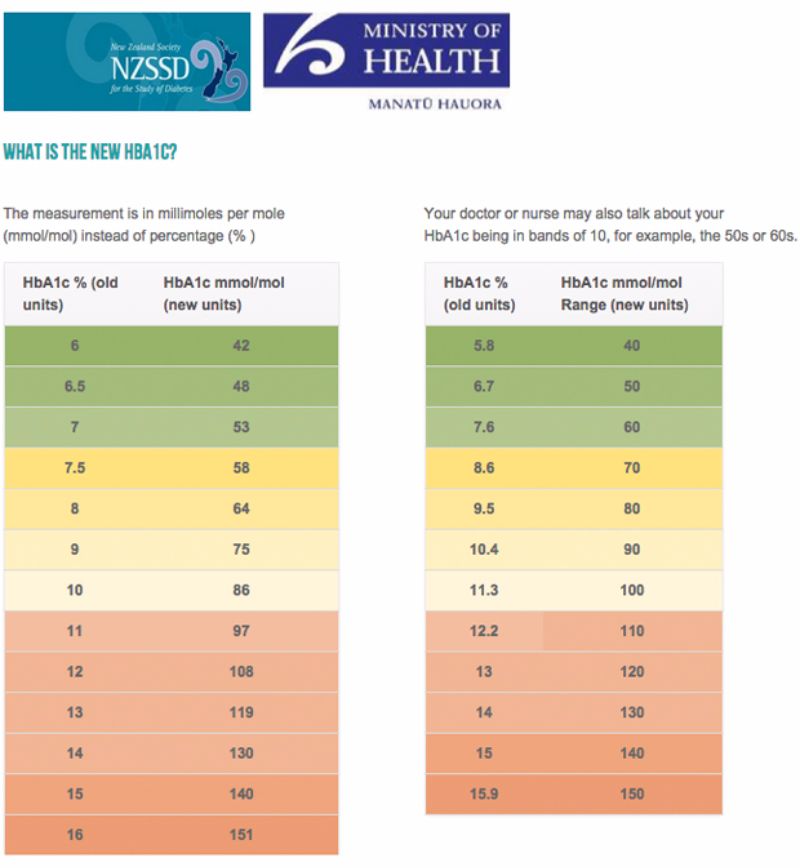
What Is My A1c If My Blood Sugar Is 119?
An estimated A1C for a blood sugar level of 119 mg/dL is around 5. 9%. Consult your doctor for precise results.
What Is A Good Blood Sugar Level In The Morning?
A good blood sugar level in the morning is between 70 and 100 mg/dL. This range indicates healthy fasting glucose. Always consult a doctor for personalized advice.
Why Is My Blood Sugar 120 In The Morning?
Morning blood sugar levels can be higher due to the “dawn phenomenon,” where hormones increase glucose production overnight. Stress, poor sleep, or late-night snacks can also contribute. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Is 119 High For Fasting Blood Sugar?
A fasting blood sugar of 119 mg/dL is considered prediabetic.
What Is Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Level?
Normal fasting blood sugar levels range from 70 to 99 mg/dL.
How To Lower Fasting Blood Sugar Naturally?
Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
Can Prediabetes Be Reversed?
Yes, prediabetes can be reversed with lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Managing fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health. A level of 119 can be a concern. Regular monitoring and a balanced diet are essential. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Stay informed and proactive to maintain optimal blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Prioritize your health for a better future.





Leave a Reply